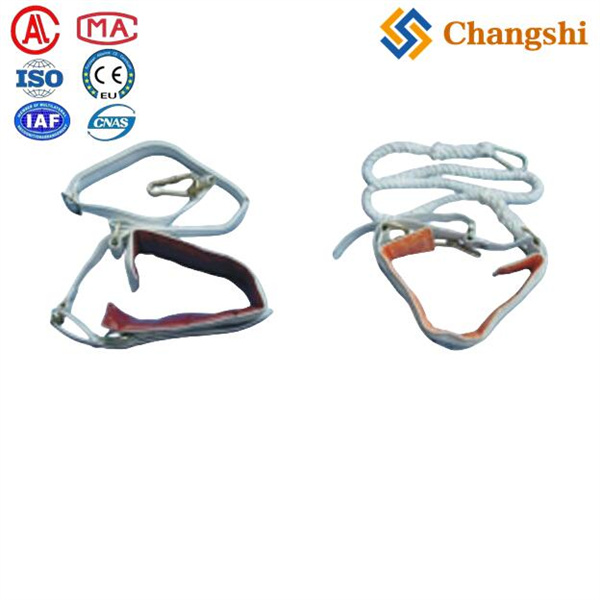
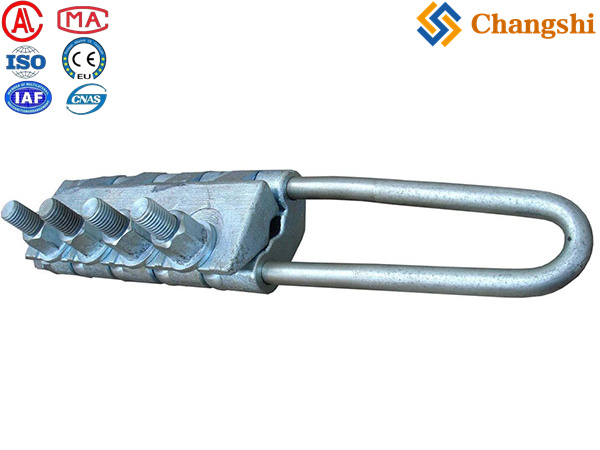
Individual Safety Auxiliary Grounding Conductor Wire For Power Transmission Line
An Individual Safety Auxiliary Grounding Wire is a dedicated grounding conductor used as a safety measure to protect personnel and equipment during electrical work or fault conditions. It provides a low-resistance path to earth, ensuring that any unintended voltage or fault current is safely dissipated, thereby preventing electric shock or equipment damage.
- Transmission Line Wire Cable Conductor Tension Stringing Equipment
- Transmission Conductor Tension Stringing Equipment For Overhead Power Lines
- Tools For Power Lines,Substation,Electrical Construction & Maintenance
- Electric Power Transmission Distribution Line Construction Machine Tools
- Overhead Power Transmission Distribution Line Repair Hardware Fittings
- Underground Cable Laying Pulling Installation Equipment Machine Tools Accessories
- Information
- Video
An Individual Safety Auxiliary Grounding Wire is a dedicated grounding conductor used as a safety measure to protect personnel and equipment during electrical work or fault conditions. It provides a low-resistance path to earth, ensuring that any unintended voltage or fault current is safely dissipated, thereby preventing electric shock or equipment damage.
-
: It is used to ground specific electrical equipment or conductive parts temporarily or permanently to ensure safety during maintenance or operation, especially in high-voltage or industrial environments.
-
:
Typically, the grounding wire should be a solid, stranded, or finely stranded copper conductor. For example, a common size is 10 mm² (6 AWG) or larger, depending on the application and local electrical codes. For substation grounding, much larger conductors like 4/0 copper wire are used. -
:
The grounding wire must be securely connected using appropriate terminals such as ring lugs, which should be double-crimped to ensure mechanical strength and electrical continuity. No insulated conductor should be visible at connection points to ensure proper strain relief and reliable grounding. -
:
According to grounding standards, working grounding wires (which include auxiliary safety grounding) are often marked with yellow and green stripes to distinguish them from protective grounding (black) and neutral wires (light blue). -
:
-
The grounding wire should be kept as short as possible to minimize resistance.
-
It should be routed with gentle bends (minimum radius of 12 inches below ground and 8 inches above ground) to avoid mechanical stress and maintain integrity.
-
Connections to grounding electrodes (ground rods or ground beds) must be clean, free of oxidation or coatings, and protected from environmental damage after installation.
-
Welding of grounding conductors should follow lap welding with sufficient overlap and multiple weld points to ensure a reliable joint.
-
-
:
Grounding electrodes and wires are usually made of galvanized steel, copper, or copper-clad steel to resist corrosion and maintain conductivity over time. -
:
Auxiliary grounding wires are essential in construction sites, substations, and during electrical maintenance to provide a temporary or additional grounding path, supplementing the main grounding system for enhanced safety. -
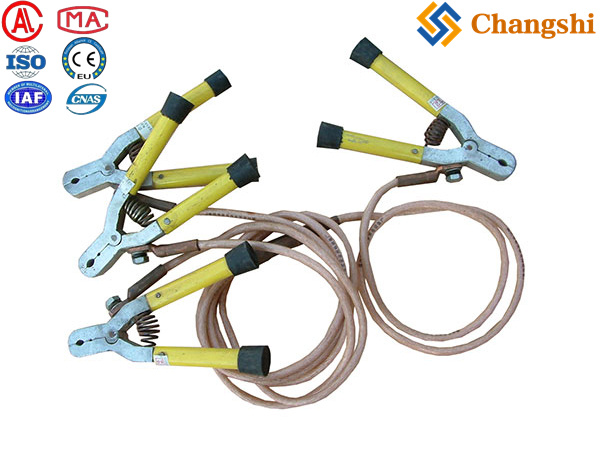


An individual safety auxiliary grounding wire is a copper conductor, sized appropriately (commonly 10 mm² or larger), with secure mechanical and electrical connections, color-coded for identification, and installed with proper routing and environmental protection. It serves as a critical safety component to prevent electrical hazards by providing a reliable path to earth for fault currents or stray voltages during electrical work or operation.
If you need specific product examples or standards compliance, many manufacturers provide auxiliary grounding wire kits designed for safe and easy installation in industrial and utility applications.